
EP.1 – How Smart Warehouses Work
What Is a Smart Warehouse?
A Smart Warehouse (also referred to as an Intelligent Warehouse) is a facility that utilizes automation and computer-controlled systems to manage operations, replacing many manual labor processes. This innovation is influenced by the concept of the Smart Factory, operating in a data-driven environment where interconnected devices work seamlessly together.
Smart warehouses integrate advanced technologies to automate every aspect of warehouse management—including order processing, goods receiving, inventory tracking, internal transport, storage, picking, sorting, and packaging—ensuring smooth, end-to-end operations with minimal human intervention. Simply put, a smart warehouse enables real-time inventory visibility, efficient stock allocation, optimized routing, and overall enhanced performance—reducing operational errors and reliance on manual labor.
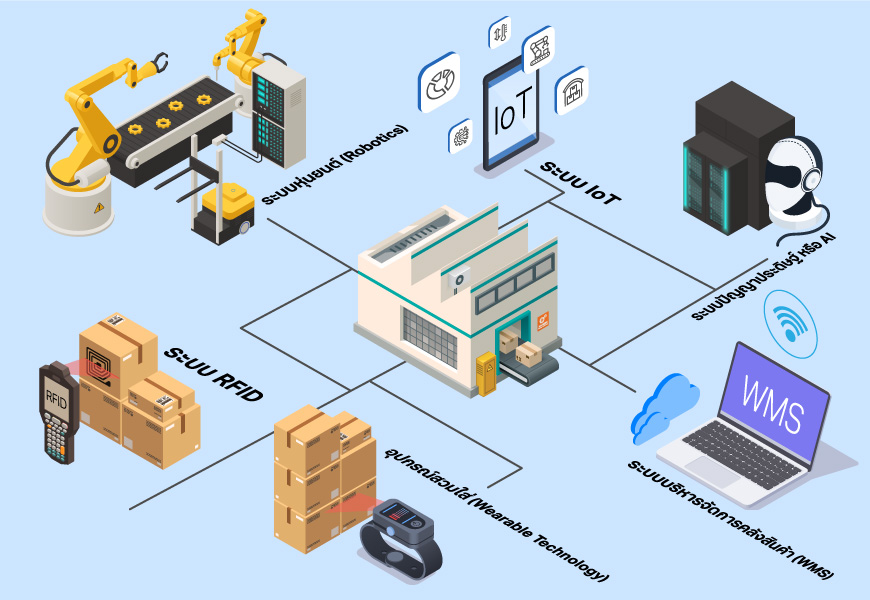
How Do Smart Warehouses Work?
Smart warehouses rely heavily on robotics, the Internet of Things (IoT), and artificial intelligence (AI) to automate processes ranging from inventory management to product retrieval. These technologies significantly reduce the need for manual labor and improve operational efficiency. Key components include:
Robotics
Many warehouse robots resemble familiar devices like robotic vacuum cleaners (e.g., Roomba) but are purpose-built for warehouse tasks. These robots are designed to transport goods from storage shelves directly to staff, replacing time-consuming manual movement.
Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT connects various devices and systems within the warehouse, enabling real-time communication and collaboration across equipment and platforms, allowing for seamless integration of operations.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI enhances productivity and accuracy by planning optimal routes for robotic movement and enabling quick item retrieval. It also analyzes item size and weight to determine the most efficient packaging methods, minimizing material use while ensuring product safety.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID)
RFID eliminates the need for traditional paper-based systems and barcode labels. Wireless tags are used instead, allowing faster scanning without needing a direct line of sight. When integrated with wearable technology and sensor systems, RFID also enables real-time product tracking throughout the warehouse.
Wearable Technology
Wearables provide warehouse staff with instant access to inventory data, allowing them to perform tasks on the floor without returning to a workstation. When combined with sensor systems, this ensures greater responsiveness and operational flow.
Warehouse Management System (WMS)
WMS is the core system that oversees all warehouse operations. It provides transparency and insight into each workflow, enabling performance tracking and continuous improvement. WMS can break down each task—such as order fulfillment—into detailed steps, monitor product movement, and generate real-time reports for warehouse managers. This enables quick identification and resolution of issues such as delays, process gaps, or picking errors.
End-to-End Efficiency
A highly efficient smart warehouse can handle all logistics activities seamlessly—from inbound goods receipt from the manufacturer to final delivery to customers—without error. The system can automatically receive customer orders, check stock availability via WMS, and, if the products are in stock, instruct robots to pick, sort, and package items for dispatch.
To achieve optimal efficiency, a smart warehouse must be:
- Fast
- Flexible
- Scalable to handle increasing demand
- And above all, transparent in data accessibility.
These qualities ensure that smart warehouses are not just technologically advanced, but also aligned with the evolving needs of modern supply chains.
The commercial, including articles and artworks shown is an intellectual property of Jenbunjerd Co.,Ltd. Unauthorized reproduction is prohibited and may subject to criminal prosecution.






